
05 Jan Internet of Things (IoT): Transforming Connectivity into Smarter Solutions
The Internet of Things (IoT) has evolved from a tech concept into an everyday reality, connecting devices across homes, industries, and cities. By collecting and acting on data in real time, IoT creates smarter systems, predictive operations, and efficient environments. Building on the ideas from our earlier blog post on The Power Of IoT, this series investigates the practical applications of these interconnected technologies.
How does IoT Link to the World?
IoT acts as the ‘eyes and ears’ of the digital world, gathering data from the real world and connecting it digitally through sensors and input devices. These sensors capture signals such as motion, temperature, location, pressure, and health-related data, transforming everyday objects into sources of meaningful digital insights. The data is sent to cloud or edge platforms, where analytics and intelligence enable automation, alerts, and well-informed decision-making — turning raw physical information into actionable digital intelligence.
This transition from physical phenomena → digital data → intelligent action is what empowers IoT systems
IoT in Everyday Life — Seamless Integration
Today, most of us interact with IoT without even realizing it. Smart lights that dim when a room is unoccupied, fitness wearables syncing with your phone, or voice assistants managing your playlist — all are powered by IoT systems that collect data and make environments responsive.
Think of IoT as an invisible digital layer that learns, adapts, and predicts, turning data into insights that improve convenience, safety, efficiency, and sustainability.
Projected Market Share — Headed by 2025
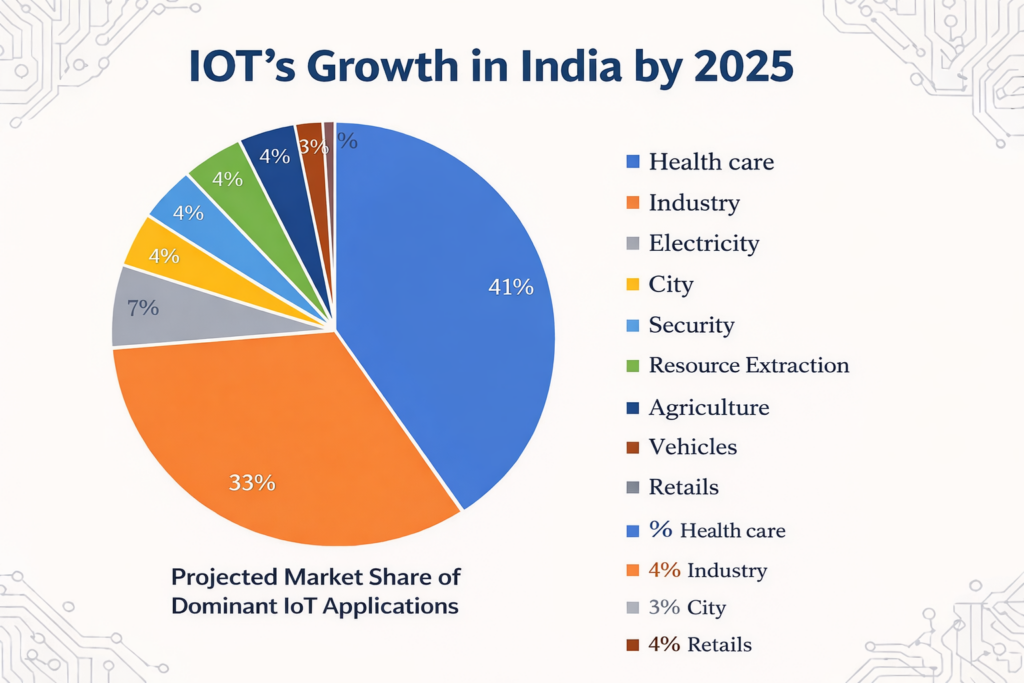
Dominant IoT applications illustrates where this technology is expected to have the greatest impact based on India:
Healthcare – 41%: IoT in healthcare uses wearable devices and smart systems to monitor health. Real-time monitoring, early detection of issues, and better patient care are key benefits. Example: Smartwatches tracking heart rate and glucose monitors sending data to doctors instantly.
Industry – 33%: IoT monitors machines, inventory, and production processes. Benefits include predictive maintenance, higher efficiency, and lower downtime. Example: Sensors detecting machine wear to schedule maintenance before breakdowns.
Electricity, City, Security, Resource Extraction, Agriculture, Vehicles, Retail – Remaining 26% collectively: IoT in these sectors enhances energy management, urban infrastructure, safety, resource optimization, agricultural efficiency, vehicle tracking, and retail operations.
This graph illustrates not just where IoT is most prevalent today, but where growth and strategic investment are occurring across various domains.
Leading IoT Application Areas
1. Healthcare
IoT has revolutionized health monitoring, enabling patients to track vital signs continuously and remotely. Wearables like smart watches now go beyond fitness, feeding realtime health data into sophisticated analytics platforms that can flag anomalies and prompt early care — cutting hospital readmissions and improving outcomes.With healthcare IoT market expansion rising rapidly, hospitals and insurers are embracing connected devices to scale telehealth and personalized care.
2. Smart Homes — The Daily Connected Experience
Smart thermostats that learn your schedule, locks you control from your smartphone, and lighting that adjusts automatically — these examples show how IoT brings intelligence and convenience into our homes. The trend toward AI-enabled home automation continues strong in 2025, with smart ecosystems focusing on energy efficiency, voice integration, and predictive comfort control.
3. Smart Farming (Precision Agriculture)
IoT sensors placed across fields collect soil moisture, nutrient levels, and weather data. Feeding this into automated irrigation and fertilization systems ensures crops get exactly what they need — lowering water use and boosting yields. Agricultural IoT adoption is part of the broader digital transformation in farming.
4. Smart Cities — RealTime Urban Optimization
City planners leverage IoT to reduce congestion, manage utilities, and improve public safety. Smart traffic lights adjust timings based on live flow data, while environmental sensors track pollution and waste levels to improve planning decisions. Smart urban infrastructure is becoming a cornerstone of sustainable living.
5. Industry & Factories
Industrial IoT is arguably the most impactful segment of IoT — often termed Industry 5.0 when combined with human-machine collaboration.
Sensors predict machine wear and schedule maintenance before failure, reducing downtime and maintenance costs. Smart factories equipped with IoT yield higher quality, safer operations, and more efficient supply chains.
Major market studies show industrial IoT as a significant force driving global IoT adoption, with software and edge platforms playing key roles.
Protocols that make IoT Communication Possible
IoT devices rely on a set of specialized protocols that efficiently exchange data:
MQTT — Designed for low bandwidth scenarios like smart homes or remote monitoring.
HTTP/HTTPS — Standard web protocols, enhanced with encryption for cloud communication.
CoAP — Lightweight, efficient communication for constrained networks.
Zigbee — Shortrange, mesh networking for home automation.
LoRaWAN — Longrange, lowpower communication ideal for agriculture and cities.
These protocols create a communication backbone that scales from microdevices to enterprise systems.
Security — An Essential IoT Foundation
Connected devices often transmit sensitive information, making them potential targets for cyberattacks. Security threats are growing more sophisticated, ranging from data interception to AIdriven automated attacks. Strengthening IoT security involves:
Authentication and encryption
Secure communication protocols
Regular updates
Network monitoring and segmentation
As IoT expands, so too must robust cybersecurity frameworks that protect users and infrastructures from exploitation.
Emerging IoT Trends
Today’s IoT landscape is shaped by several forward-looking trends:
AIoT — The Fusion of AI and IoT: Artificial Intelligence integrated with IoT (AIoT) enables devices not just to collect data, but interpret and act on it autonomously. From predictive maintenance in factories to adaptive traffic management in cities, AIoT accelerates real-time decisionmaking and reduces human intervention.
5G and Enhanced Connectivity: Deployments of 5G networks massively expand IoT capacities — providing higher speeds, lower latency, and the ability to connect more devices simultaneously. This accelerates applications in logistics, transportation, healthcare, and more.
Sustainability and Energy Management: Sustainability is important today, and IoT helps save energy. Sensors can turn off lights or cool down when rooms are empty. Energy-saving networks like LTE-M and NB-IoT support this, and tools like Things data help organizations monitor energy use, reduce waste, cut costs, and protect the environment.
The Road Ahead – Transforming IoT
The future of IoT goes beyond connectivity. It’s about autonomy, adaptation, and insight, shaped by:
Deep integration with AI and edge platforms
Broader 5G and satellite connectivity
Intelligent data orchestration in real time
Securityfirst architectures
Expanded enterprise and consumer adoption
The IoT market is set to grow huge, with trillions in value and billions of connected devices. IoT is now essential for digital transformation and innovation in every domain.
Conclusion:
The Internet of Things has evolved from a collection of smart gadgets into a robust, intelligent ecosystem powering realtime insights, autonomous systems, and responsive environments. From hospitals and factories to homes and cities, IoT reshapes how people live and how enterprises operate.
With advanced protocols, integrated intelligence, robust security, and growing connectivity, IoT stands as a cornerstone of the digital future — one that is safer, smarter, and deeply interconnected.

Sorry, the comment form is closed at this time.