
29 Jan Healing Beyond Screens: The Rise of AR & VR Telemedicine
Telemedicine powered by Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR) is transforming the way healthcare is delivered. It brings medical services directly to patients, making treatment more interactive, understandable, and effective — all without the need to physically visit a hospital or clinic.
The healthcare industry is rapidly evolving, and telemedicine has become a significant part of this transformation. Earlier, telemedicine allowed patients to consult with doctors remotely through video or phone calls. But now, with the integration of AR and VR technologies, virtual healthcare has entered an advanced stage, offering more realistic, engaging, and accurate medical experiences for both doctors and patients.
What is Telemedicine?
Telemedicine refers to the delivery of healthcare services remotely using digital communication technologies. It enables patients to consult doctors remotely, get diagnosed, and monitor health conditions, even without visiting a clinic.
This approach is especially beneficial for:
- People living in rural or remote areas
- Patients with mobility issues or chronic illnesses
- Elderly individuals who require frequent medical attention
- Emergency situations such as pandemics (e.g., COVID-19)
Telemedicine improves accessibility, convenience, and response time, ensuring that quality healthcare reaches people when and where they need it most.
Role of AR and VR in Telemedicine

Augmented Reality (AR) involves the overlay of digital information upon the real world, whereas Virtual Reality (VR) creates a completely immersive, computer-generated environment. When combined with telemedicine, these technologies significantly enhance virtual healthcare experiences.
As telemedicine continues to evolve with technologies such as Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR), the reliability of medical equipment has become more critical than ever. Platforms like Equicare play a key role in enabling virtual healthcare by ensuring that medical devices, diagnostic tools, and connected systems remain safe, fully functional, and always ready for use. By maintaining the backbone of healthcare infrastructure, Equicare helps deliver seamless and uninterrupted telemedicine experiences for both patients and healthcare providers.
How AR and VR Improve Telemedicine
Augmented reality(AR) adds digital information to the real world, while Virtual reality(VR) immerses users in a fully simulated environment, such as:
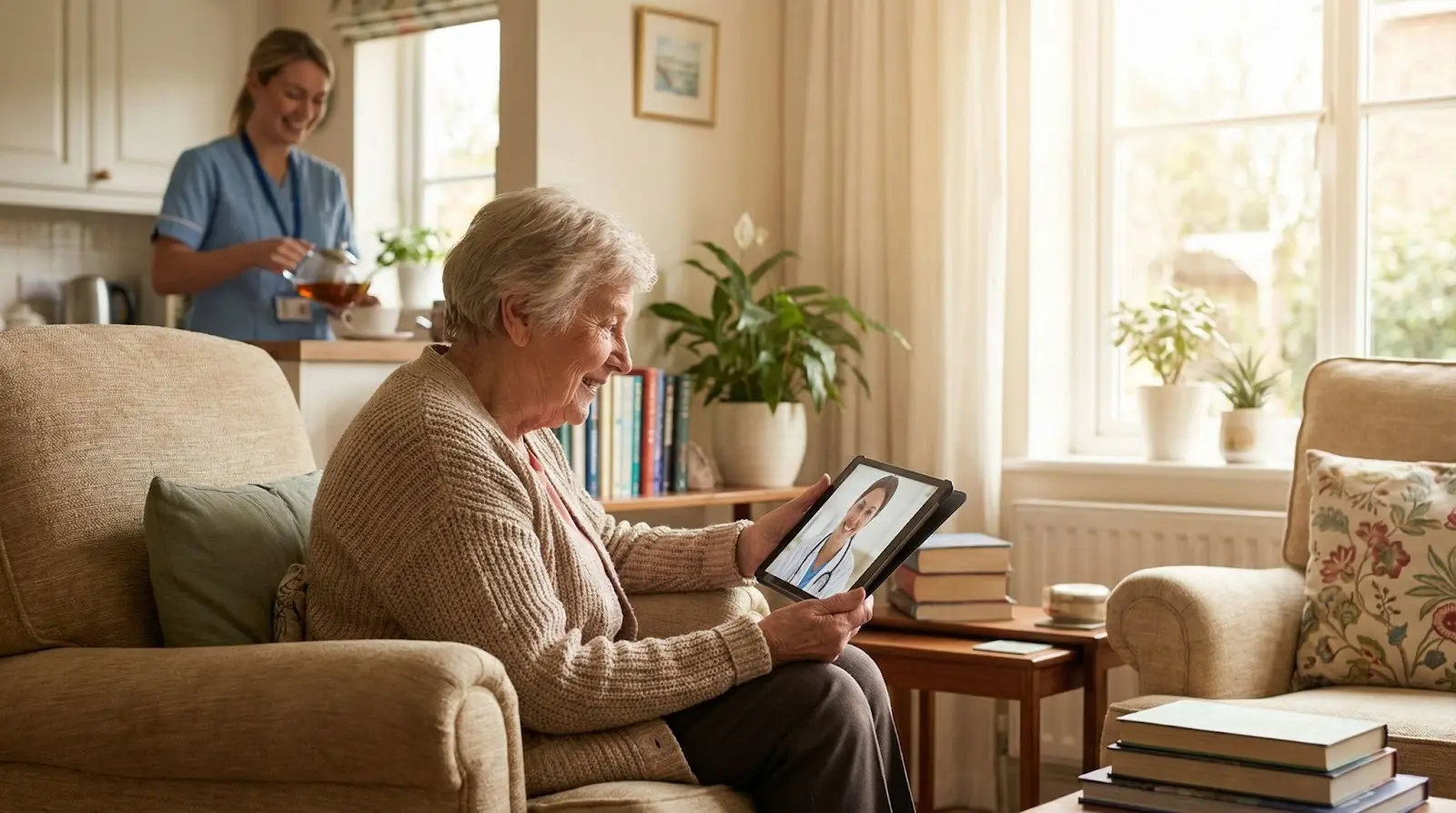

1. Better Consultations
With the integration of VR and AR, telemedicine is transforming into a more interactive and immersive healthcare experience. Making remote consultations feel more personal and close to real-life visits. This real-time access to data helps doctors make faster, more accurate decisions, improves consultation quality, and enhances overall patient care — bridging the gap between virtual and in-person healthcare.
2. Training and Remote Surgeries
AR and VR enable support surgical guidance. Surgeons can perform operations using AR overlays that provide real-time guidance, overlaying anatomy visuals, or step-by-step instructions. VR, on the other hand, allows medical students and professionals to practice complex surgeries in a safe, simulated environment before performing them on real patients.
This reduces errors, improves precision, and increases confidence among healthcare professionals.
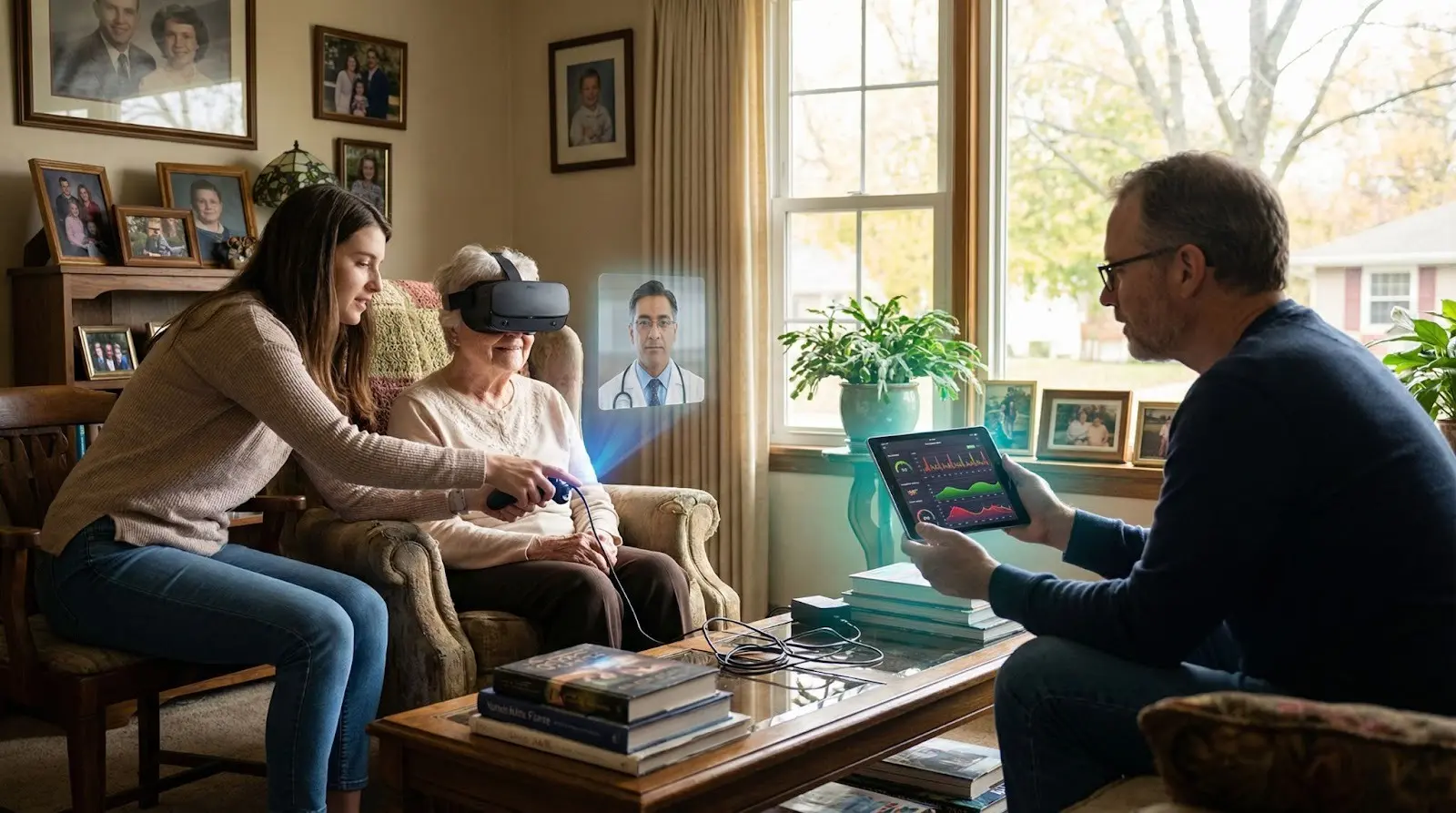
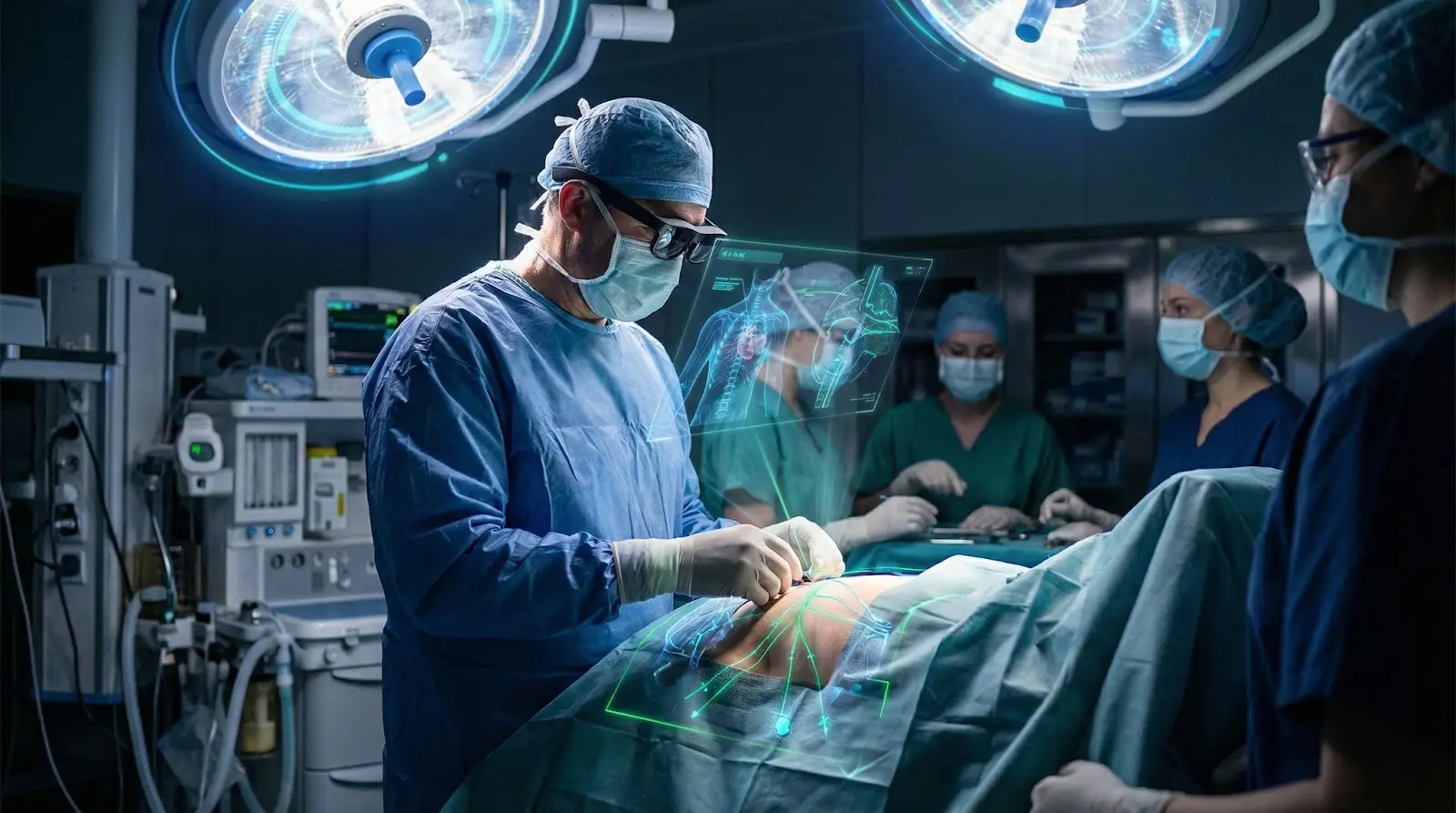

3. Improved Patient Care and Therapy
VR can simulate medical conditions, helping patients better understand their diagnosis and treatment plan. In mental health care, VR therapy is used to treat anxiety, stress, and phobias by placing patients in controlled virtual environments. AR applications also assist patients with home-based recovery exercises, providing real-time guidance and feedback, reducing the need for frequent clinic visits.
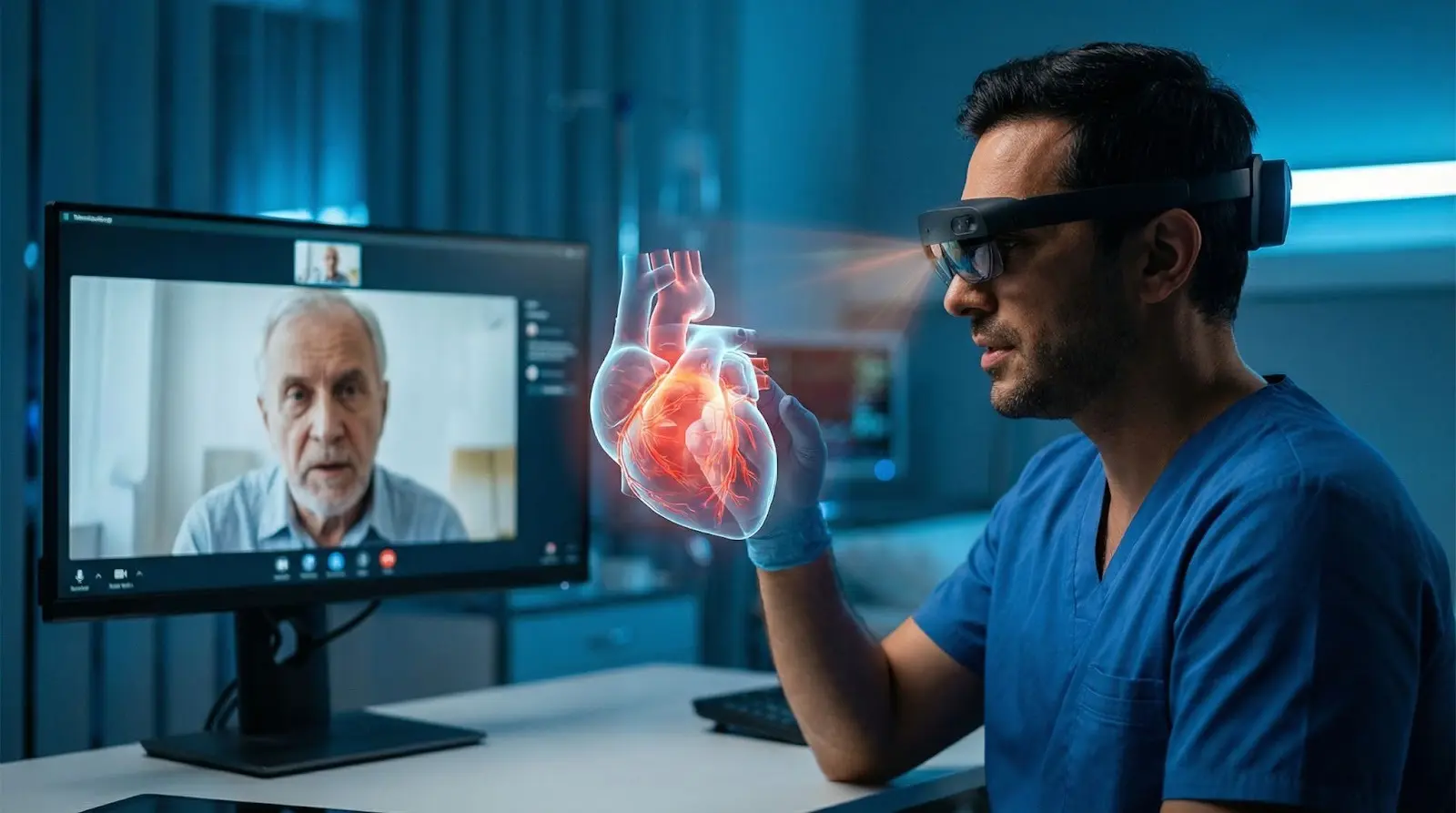
4. Enhanced Diagnosis & Visualization
AR tools help assist doctors in visualizing internal organs, fractures, or tumors during remote consultations. For example, a cardiologist could use AR to see 3D heart models to explain heart conditions and treatment options clearly.
This improves understanding, builds patient trust, and supports more accurate diagnoses.
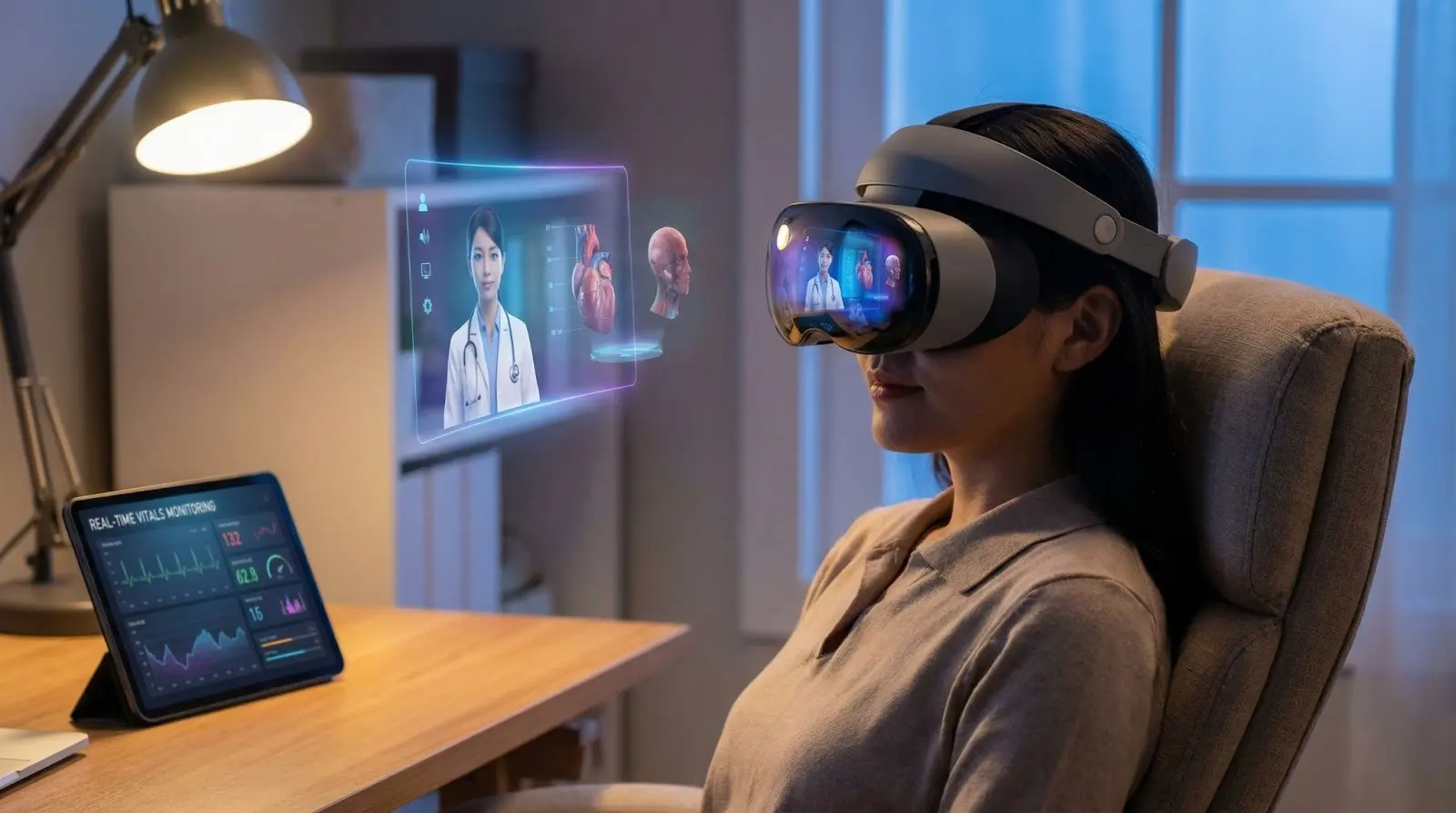


5. Remote Monitoring and Preventive Care
AR and VR can be integrated with wearable devices to monitor: Heart rate, Blood pressure, Oxygen levels, Physical movements. Doctors can track patient health remotely and provide timely advice, enabling early detection and preventive care, which reduces hospital admissions.
Benefits of Telemedicine with AR and VR
· Convenience and Comfort: Makes healthcare easier to access from home.
· Improve accessibility: Patients in remote areas can access specialized healthcare.
· Cost and Time Saving: Reduces travel time, waiting periods and extra expenses for both patients and doctors.
· Enhanced Health Management: Helps track and manage health more effectively.
· Patient Engagement: Immersive experiences improve understanding and encourage better follow-through with treatments.
· Reduced Hospital Load: · Convenience and Comfort: Makes healthcare easier to access from home.
· Improve accessibility: Patients in remote areas can access specialized healthcare.
· Cost and Time Saving: Reduces travel time, waiting periods and extra expenses for both patients and doctors.
· Enhanced Health Management: Helps track and manage health more effectively.
· Patient Engagement: Immersive experiences improve understanding and encourage better follow-through with treatments.
· Reduced Hospital Load: Helps hospitals manage patient flow more effectively
Real-Life Examples
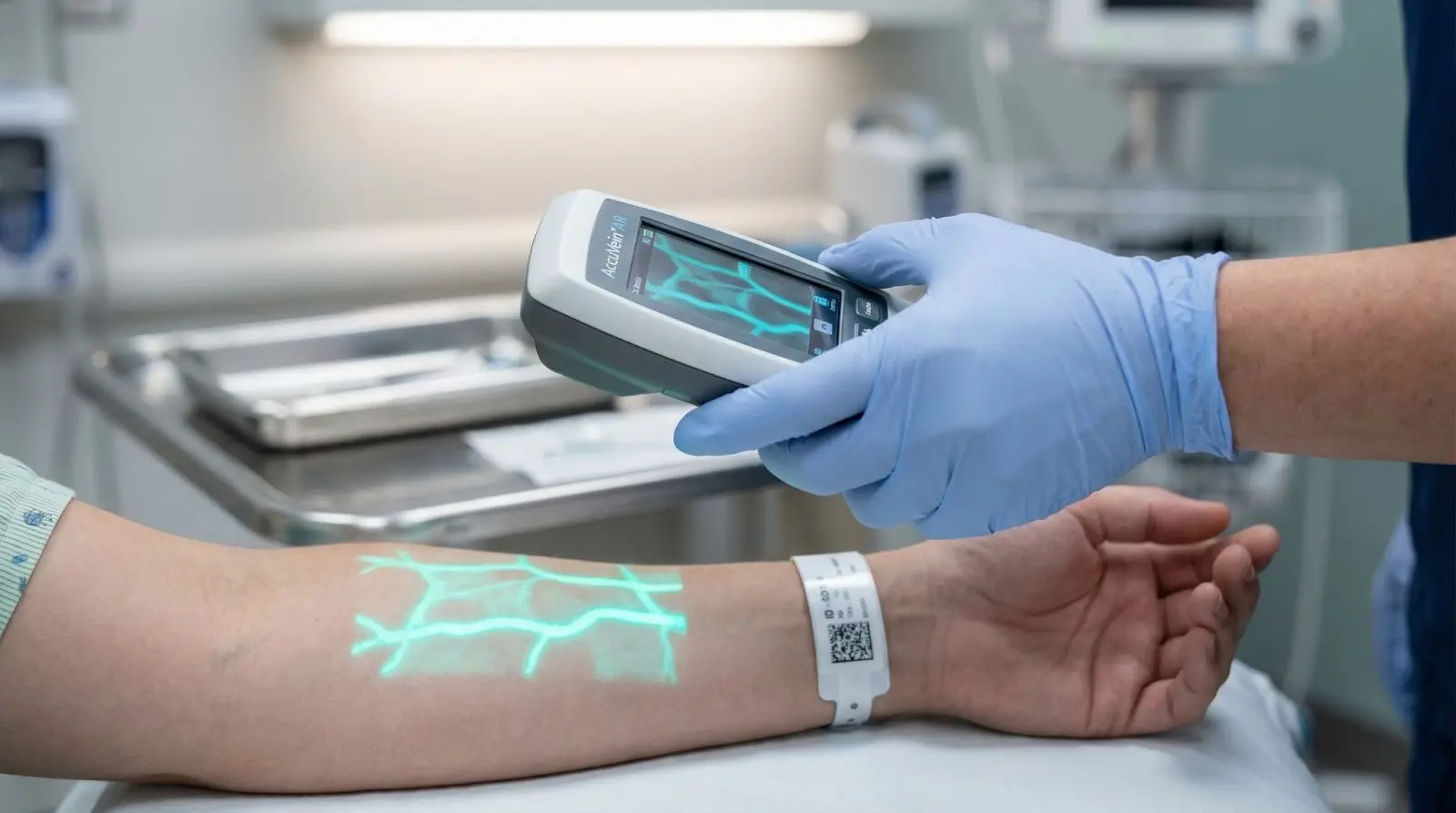
· AccuVein (AR Tool)
AccuVein uses augmented reality to project a map of veins onto a patient’s skin. This helps nurses find veins quickly for injections or blood tests, reducing pain and improving patient comfort.
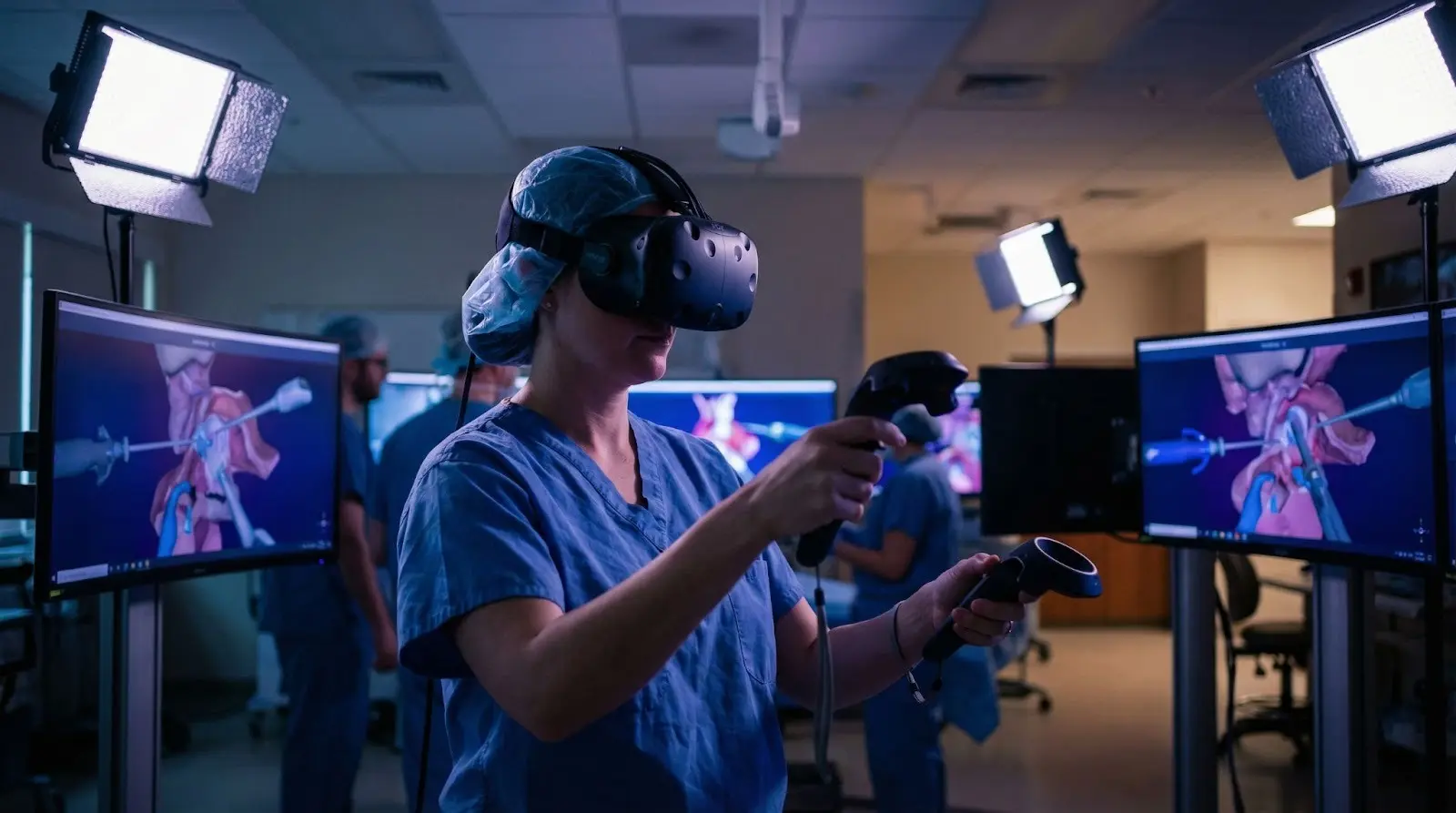


· Osso VR(VR platform):
Osso VR is a virtual training platform used by surgeons. It allows doctors and medical students to practice surgeries in realistic 3D environments before working with real patients.
· AppliedVR (VR Therapy):
A VR-based therapy that helps patients manage pain, stress, or anxiety. For example, a patient can wear a VR headset and be transported into a calm, relaxing virtual world during treatment.

Challenges and Future Outlook
While the potential is huge, there are challenges:
· High Costs: The expense of AR/VR hardware and specialized equipment makes it difficult to make a widespread solution.
· Infrastructure: Reliable, high-speed internet connections are essential, which can be a challenge in rural areas.
· Technical Limitations: Current devices and software still have performance and compatibility issues.
· Training: Doctors and staff need proper training to effectively use AR/VR tools.
· Privacy and Security: Patient data must be protected in virtual platforms to maintain trust.
Even with these challenges, AR and VR in telemedicine are growing quickly. As the technology becomes more affordable and user-friendly, virtual healthcare may soon become a standard part of medical practice, just like smartphones have become a normal part of our daily lives.
Frequently Asked Questions:
Q1. What is telemedicine?
Telemedicine is remote healthcare delivered through digital platforms like video calls and mobile apps.
Q2. How does telemedicine benefit patients?
It saves time, reduces travel, and provides quick access to medical care from anywhere.
Q3. Is telemedicine safe and reliable?
Yes, when supported by secure systems and well-maintained medical equipment.
Q4. What services can be provided via telemedicine?
Consultations, follow-ups, prescriptions, mental health support, and chronic care management.
Q5. What is the future of telemedicine?
It will expand with AI, wearables, and advanced remote monitoring technologies.
Conclusion:

Telemedicine with the integration of AR and VR is not just a concept about the future because it is already here with us and is adding value to remote healthcare by providing patients and doctors with improved healthcare services and an efficient healthcare experience.
With innovations occurring on a continuous basis, virtual healthcare is bound to become easier, smarter, more interactive, and universally accessible, helping to create the future healthcare system for the world.


Sorry, the comment form is closed at this time.