
12 Feb Atomic Clock: The Most Accurate Timekeeper Ever Created
Introduction
Time controls everything — from phone networks and GPS navigation to stock markets and space missions. But have you ever wondered how the world keeps time so perfectly aligned? The answer lies in atomic clocks, the invisible systems that silently synchronize our modern world.
Unlike regular clocks that rely on gears or vibrations of quartz crystals, atomic clocks measure time using the natural vibrations of atoms. This makes them unbelievably accurate — so precise that they won’t lose even one second in millions of years, making them the gold standard of global timekeeping.
What is an Atomic Clock?
An atomic clock is the most accurate time-keeping device, developed by man, which measures time by monitoring the constant frequency of atoms (usually cesium or rubidium) to measure time.
Instead of ticking like a wall clock or oscillating like a quartz watch, atomic clocks track how atoms absorb and release energy. These atomic motions are constant everywhere in the universe, which makes atomic clocks globally reliable.
In fact,one second is officially defined by atomic clocks as:
The time taken for a cesium-133 atom to vibrate9.192.631.770 times.
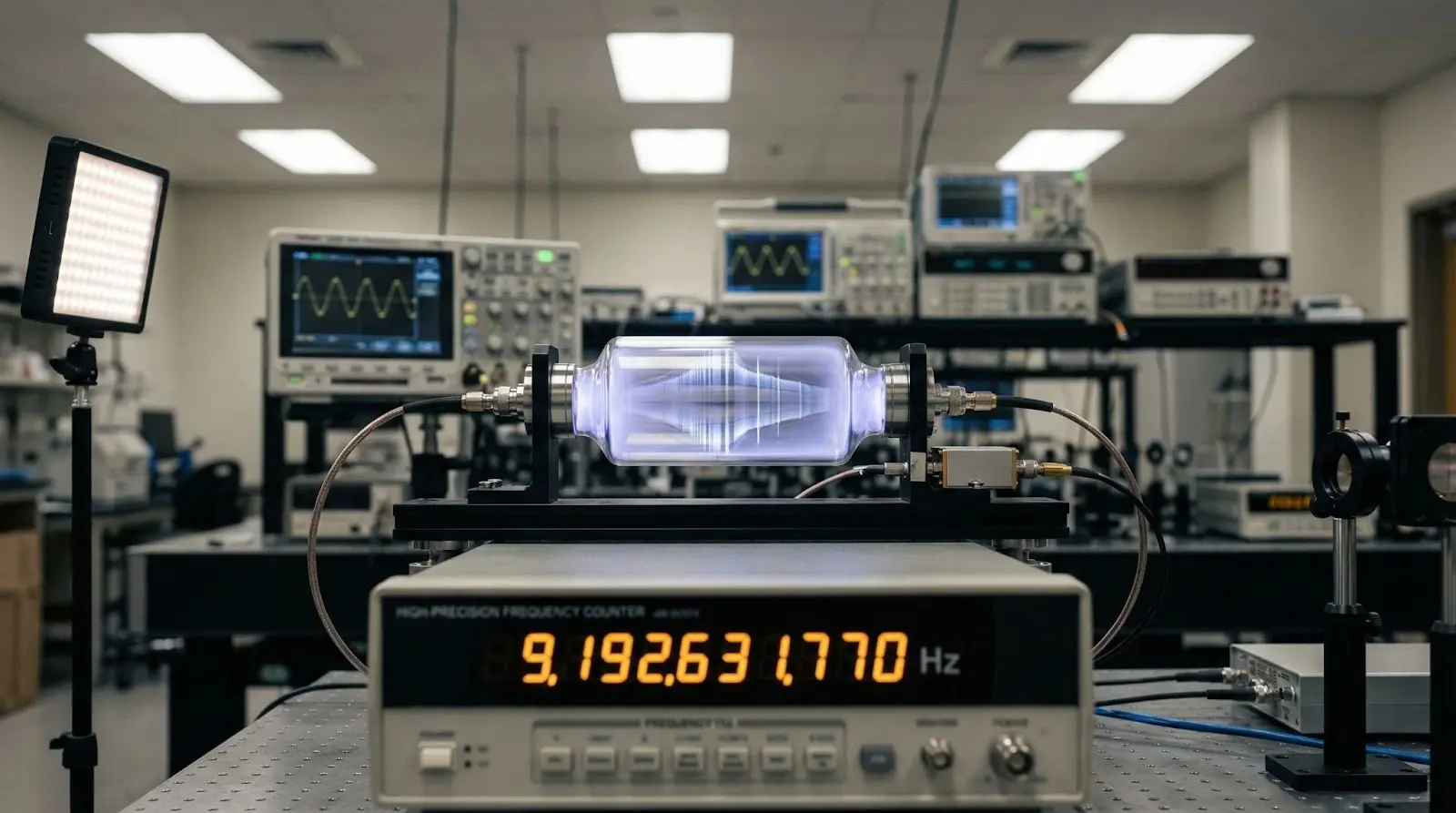

How Does an Atomic Clock Work?
At its core, an atomic clock follows three simple steps:
1. Atoms are energized using microwaves or lasers.
2. The clock detects the exact frequency at which atoms change energy states.
3. This frequency is counted and converted into seconds.
When the frequency matches perfectly, the clock knows it is measuring time accurately.
Think of it like tuning a radio:
When the signal is perfectly clear, you’re locked onto the exact station — atomic clocks do the same with atomic vibrations.
Core Principles Behind Atomic Clocks
Atomic clocks are based on a few powerful scientific principles:
1. Atomic Consistency: Atoms behave the same way anywhere in the universe. A cesium atom in India vibrates exactly like one in space.
2. Quantum Energy Levels: Atoms absorb and emit energy only at specific frequencies. This makes them perfect natural oscillators.
3. Frequency Over Mechanics: Instead of mechanical motion, atomic clocks use electromagnetic frequency, which is far more stable and precise.
The Mechanism Explained Simply
Here’s a simplified breakdown of the internal mechanism:
- Atoms are placed inside a vacuum chamber.
- A microwave or laser excites the atoms.
- Sensors check whether the excitation matches the atom’s natural frequency.
- Feedback systems fine-tune the signal.
- The stable frequency output becomes the clock’s time signal.
No ticking parts. No wear and tear. Just pure physics at work.
Advanced Technologies Used Today
Modern atomic clocks have evolved far beyond early designs:
Optical Atomic Clocks
These use lasers instead of microwaves and are 100 times more accurate than traditional atomic clocks.
Atomic Fountain Clocks
Atoms are cooled using lasers and tossed upward like a fountain, allowing longer measurement time and higher accuracy.
Chip-Scale Atomic Clocks (CSAC)
Tiny atomic clocks small enough to fit on a circuit board—used in defense systems, satellites, and secure communications.
Applications and Real-World Uses
Atomic clocks silently power modern life:
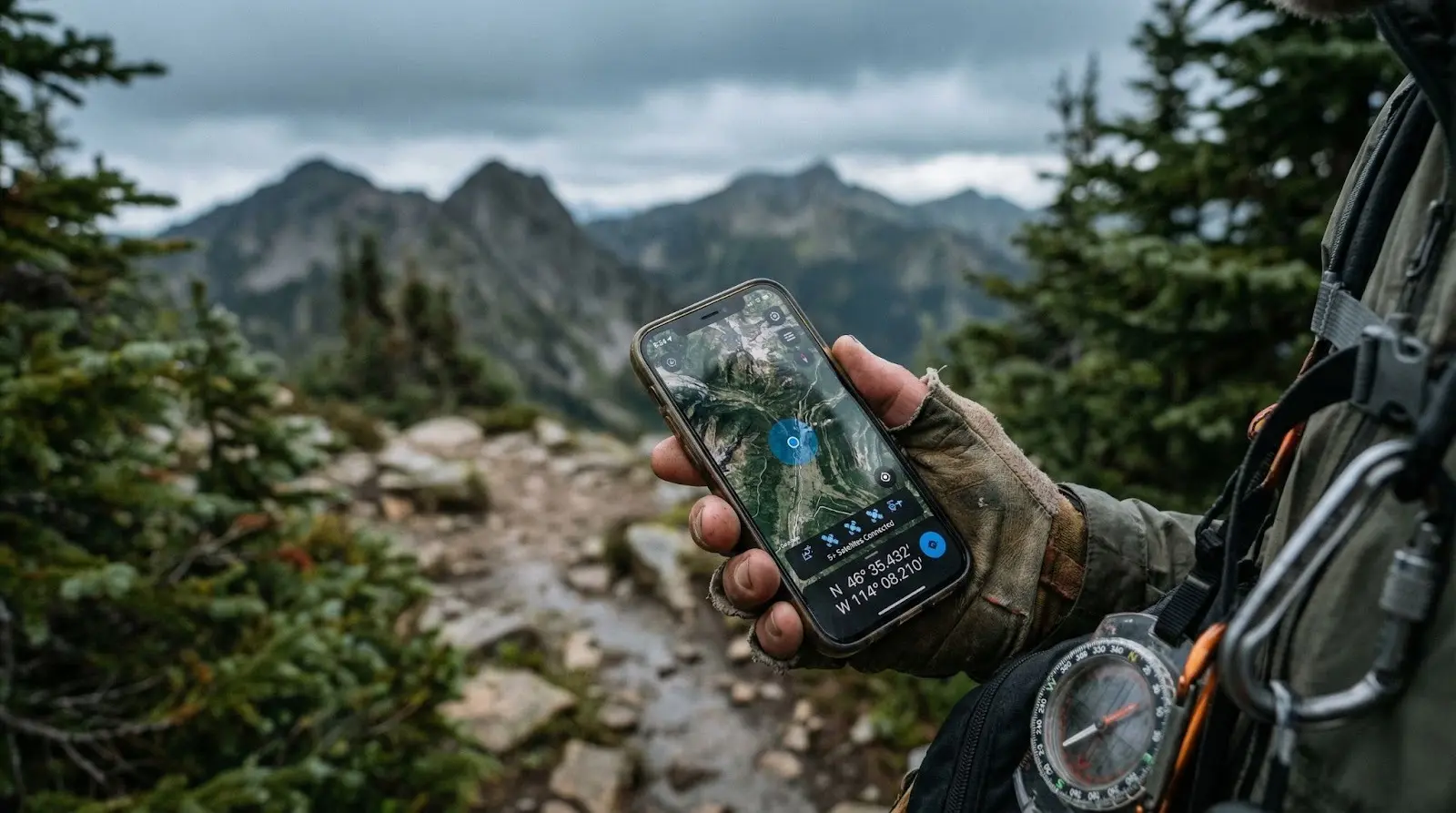

GPS Navigation
Your phone’s location accuracy depends on atomic clocks in satellites.
Internet & Telecom
High-speed data transfer and network synchronization rely on precise timing.
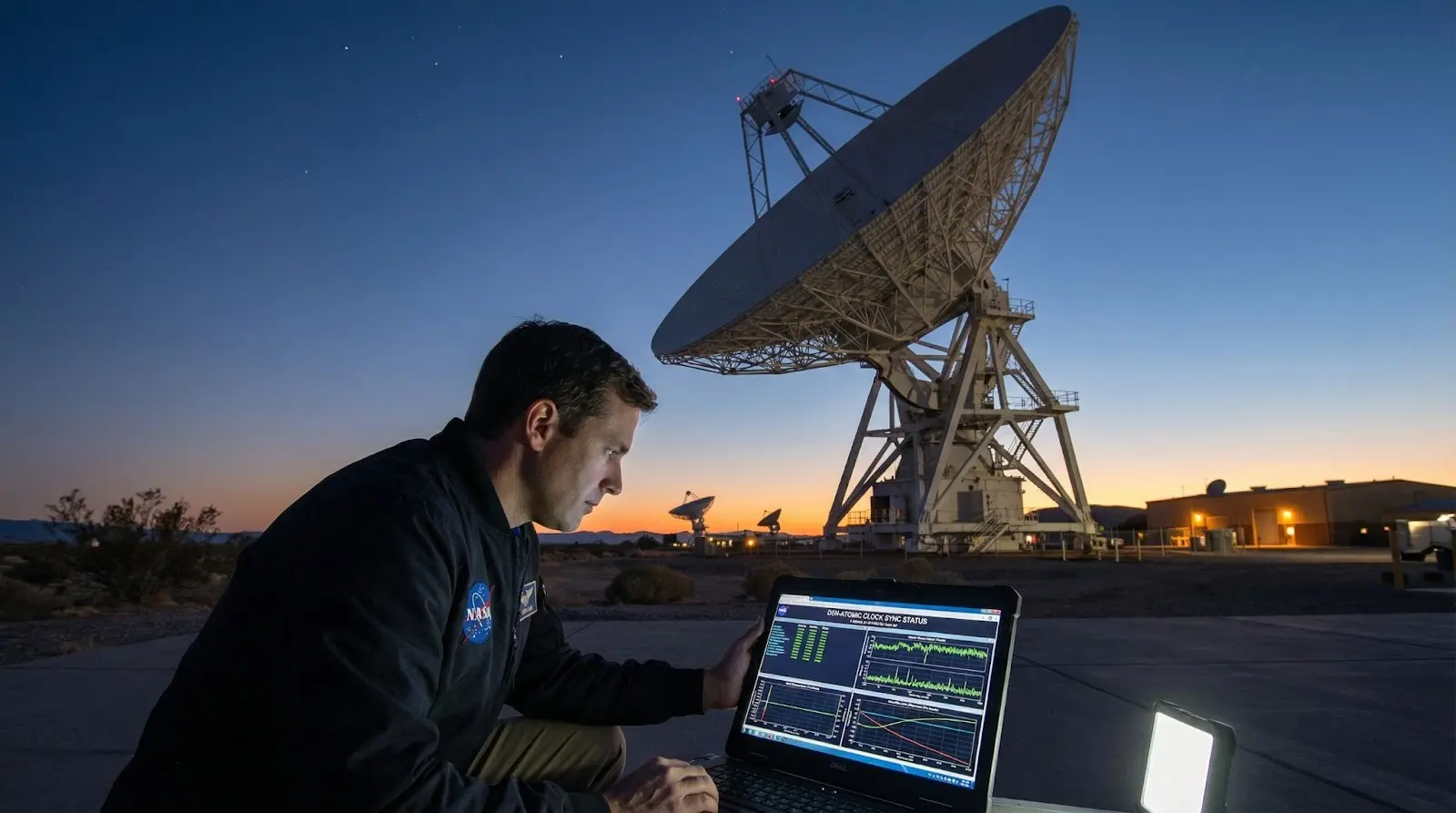


Space Exploration
Deep-space missions require atomic clocks to navigate vast distances.
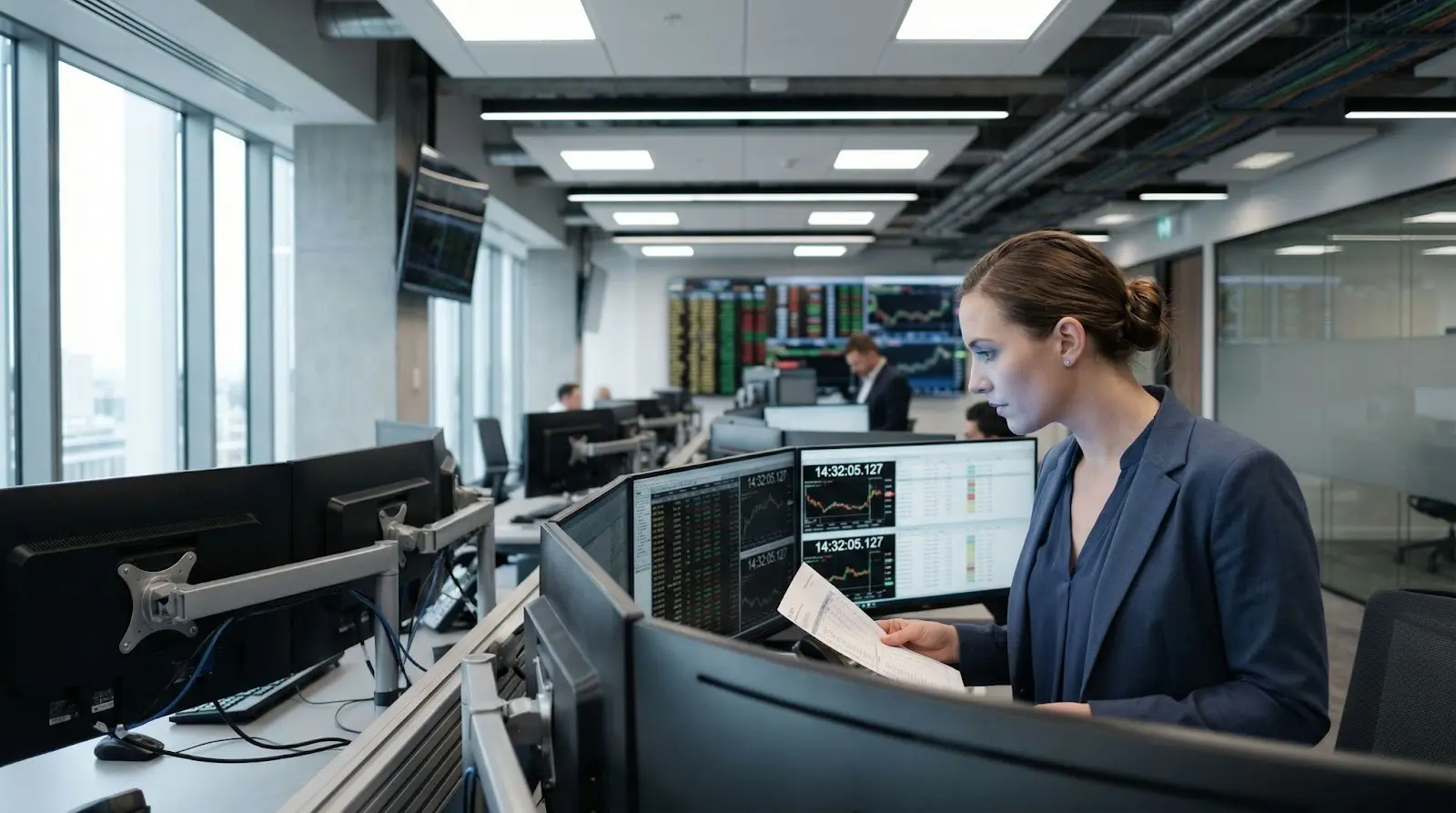
Banking & Stock Markets
Timestamp accuracy prevents fraud and ensures fair trading.

Scientific Research
Used in testing relativity, gravitational waves, and fundamental physics.
Can You Buy an Atomic Clock?
Yes — but not the lab-grade ones you see in research facilities. Commercial Options Include:
- Radio-controlled atomic clocks for homes and offices
- Network-synced atomic clocks for telecom and data centers
True laboratory atomic clocks cost lakhs or crores of rupees and require controlled environments, making them suitable only for governments and research labs.
The Future Scope of Atomic Clock
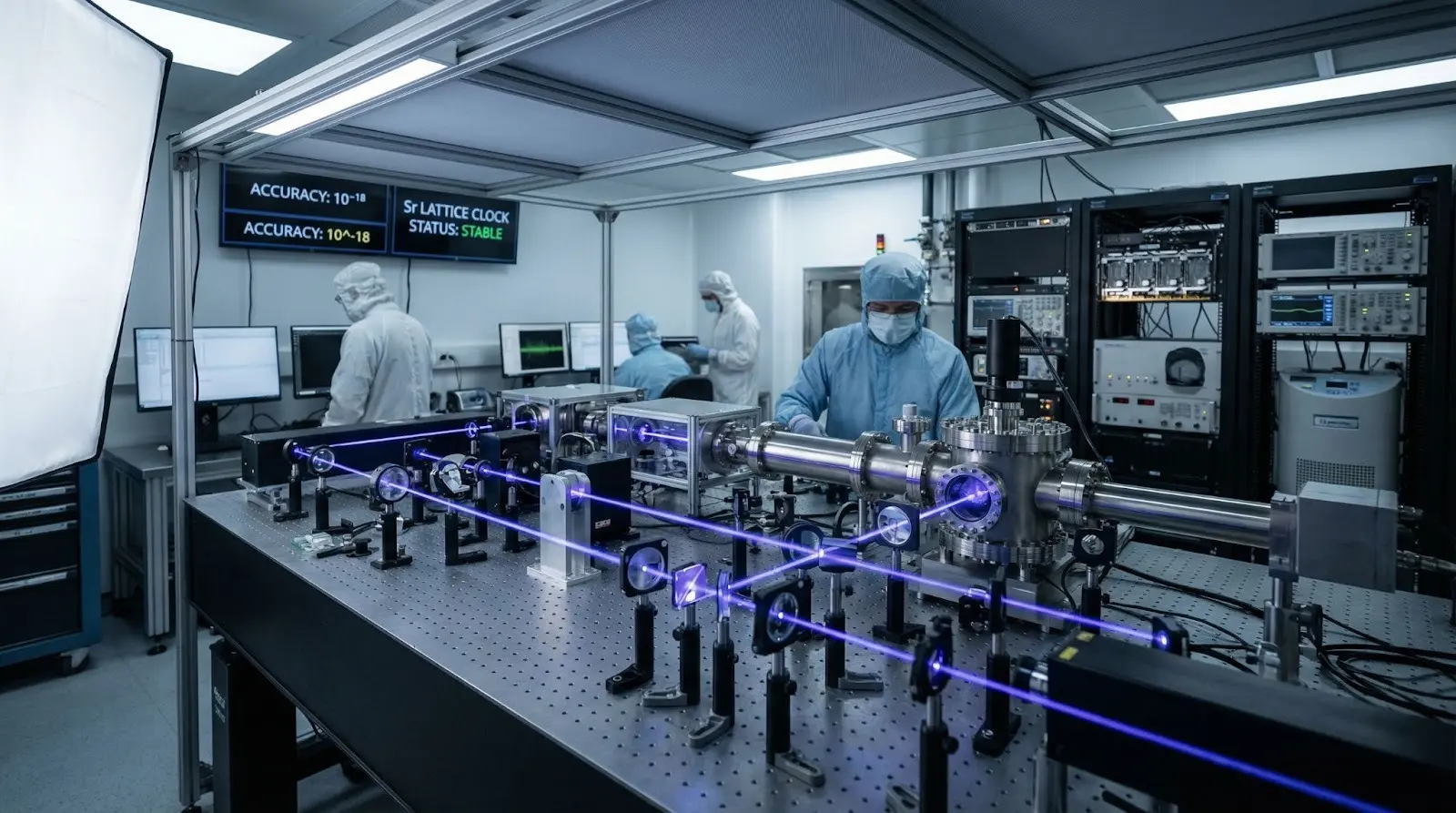

The future of atomic clocks is moving toward extreme precision and real-world deployment. New optical atomic clocks are so accurate they can measure tiny gravitational changes, improving GPS accuracy, satellite navigation, and next-generation 6G communication systems. Researchers are also working on making these clocks smaller and portable, allowing their use beyond laboratories in space missions, defense systems, and autonomous technologies.
In the coming years, nuclear clocks may surpass current atomic standards and potentially redefine the global unit of time. With applications expanding into space exploration, climate monitoring, and secure digital infrastructure, atomic clocks are set to become a key driver of future scientific discovery and advanced technology.
Frequently Asked Question (FAQs):
1. What is an atomic clock?
An atomic clock is a highly accurate timekeeping device that measures time using the natural vibrations of atoms, usually cesium or rubidium.
2. When was the atomic clock invented?
The first atomic clock was developed in 1949, and the cesium atomic clock became the global time standard in 1955.
3. Where can you buy an atomic clock?
Consumer atomic clocks can be purchased online from e-commerce platforms and electronics stores, while laboratory-grade atomic clocks are available only to research institutions and government agencies.
4. Where are atomic clocks located?
Atomic clocks are located in national laboratories, space satellites, research centers, and are also used in GPS systems and telecom networks worldwide.
5. Why are atomic clocks so important today?
Atomic clocks are essential for GPS navigation, internet synchronization, satellite communication, financial systems, and scientific research due to their extreme accuracy.
Conclusion
Atomic clocks are the silent backbone of modern civilization.
From guiding satellites to securing financial systems, they define time with unmatched precision. As technology advances, atomic clocks will not just measure time — they will shape the future of navigation, science, and space exploration.
In a world that never stops moving, atomic clocks make sure time never slips.

Sorry, the comment form is closed at this time.