05 Feb The Next AI Breakthrough: Photonic Chips
Introduction
What if computers could process information at the speed of light instead of electricity?
That is now possible with the photonic chips.
With the advent of the modern digital era in the growth of AI, big data, cloud computing, and 5G/6G networks, traditional electronic chips are reaching their limits. They are consuming more power, producing more heat, and struggling with ultra-high data speeds. To overcome these challenges, scientists and engineers are turning to Photonics — the science of light.
Photonic chips use light (photons) instead of electricity (electrons) to transmit and process data.
What Is a Photonic Chip?
A photonic chip or optical chip, is a microchip that transmits light signals to carry, process, and store data instead of electrical signals.
Just like electronic chips guide electrons through wires, a photonic chip directs light through optical waveguides on the chip. These waveguides control how light moves, splits, combines, or changes — allowing data processing at extremely high speeds.
In simple terms:
- Electronic chip = data through electrons
- Photonic chip = data through light
Basic fundamentals of Chip
Photonic chips are built using photonic integrated circuits (PICs), combining multiple optical components on a single chip. Key building blocks include:
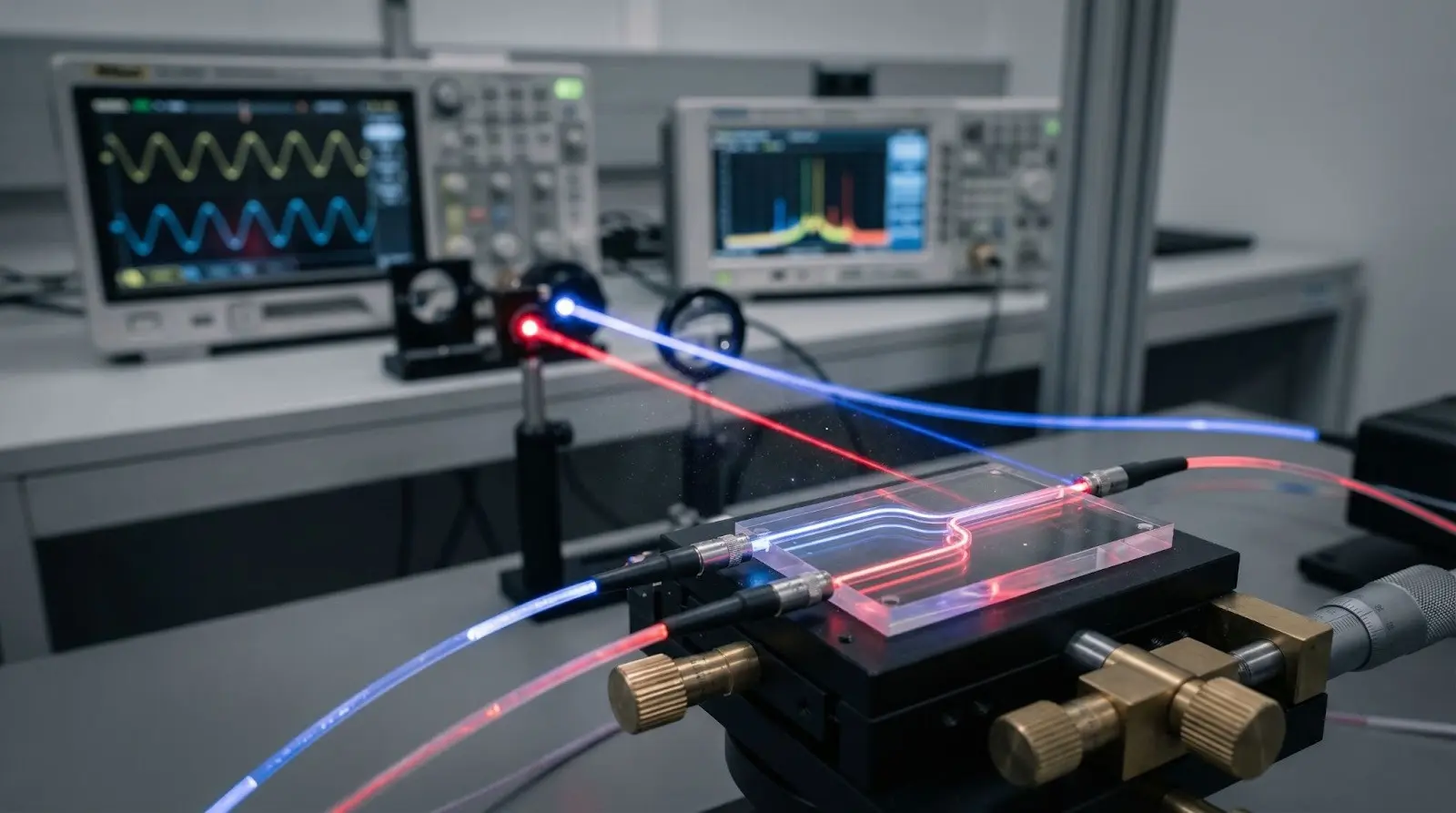
Light Source – Lasers that generate light
Waveguides – Paths that carry light on the chip
Modulators – Convert electrical signals to light signals
Detectors – Convert light signals back to electrical signals
Optical Switches – Control the flow of light
Photonic chips function on the basis of principles such as reflection, refraction, interference, and diffraction. Since light travels extremely fast and faces no electrical resistance, photonic chips can handle massive data rates efficiently.
Material use in Photonic chip
Common materials used to manufacture photonic chips include:
- Silicon – Most widely used (silicon photonics)
- Indium Phosphide (InP) – Used for high-performance lasers
- Gallium Arsenide (GaAs) – Used in optical communication
- Silicon Nitride – Low-loss optical waveguides
Silicon is popular because it is compatible with existing semiconductor manufacturing methods.
Data Transmission and processing
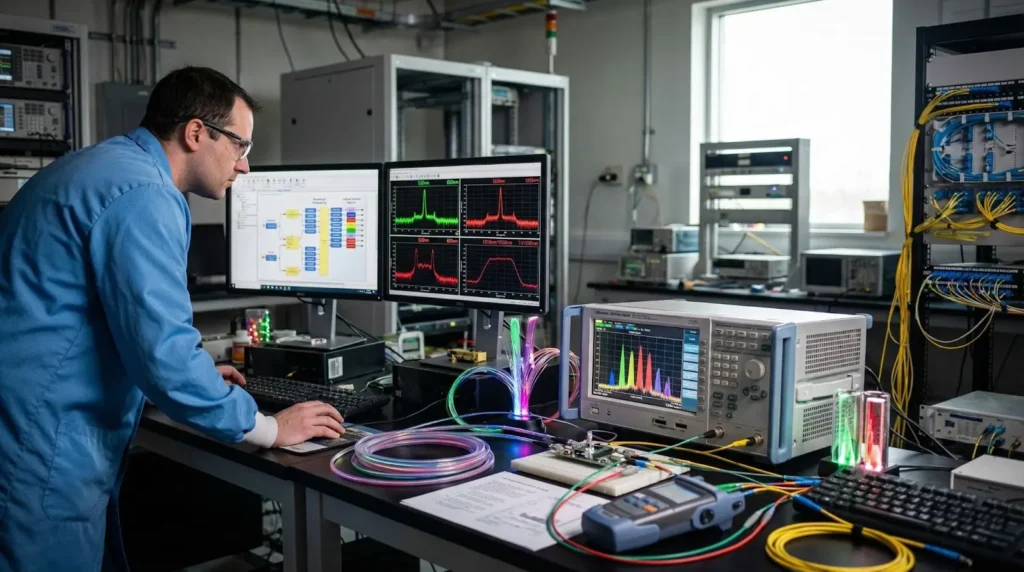

In photonic chips, optical data transmission is performed through light pulses. Various data bits are expressed by variations in Light intensity, Wavelength (color of light), or Phase and polarization. This process enables parallel data transmission, in which multiple data streams are transmitted simultaneously through high speed optical interconnects. Such optical communication on chip supports ultra fast data transfer technology and emphasises the importance of photonic chips in data transmission, which is difficult to achieve using traditional electronic chips.
Leading Photonic Chip Makers and Applications
Several global companies are pioneering photonic chips and photonic integrated circuits (PICs), targeting data centers, AI, optical networking, and next-generation computing.
Global Leaders:
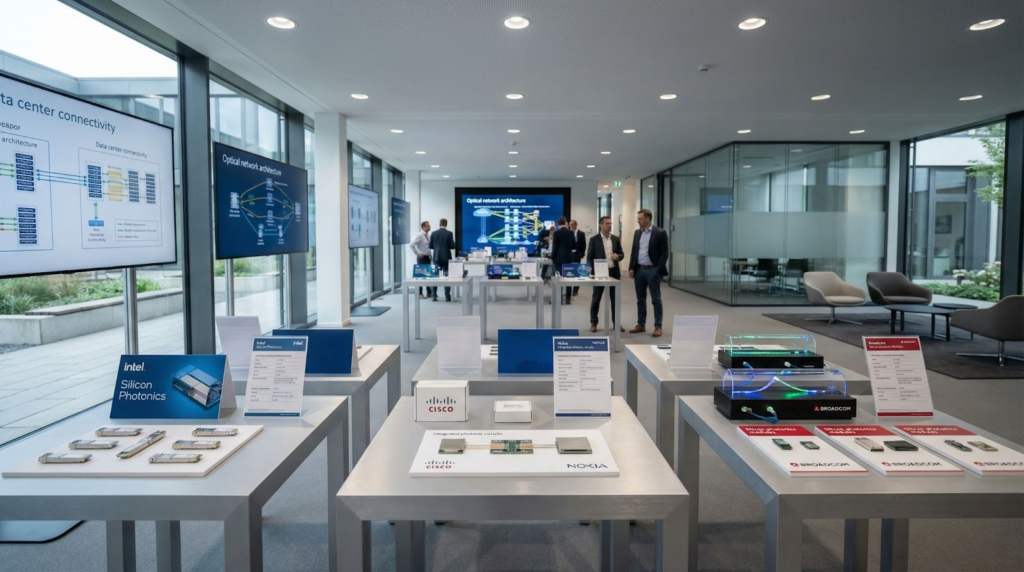

- Intel – Silicon photonics for data centers, enabling high-speed, low-power optical transfer
- IBM – Optical and photonic computing research, including AI and quantum systems
- NVIDIA – Optical interconnects for high-performance AI computing
- Cisco – Photonic chips for optical networking and high-speed communication
- Broadcom – High-speed optical chips and co-packaged optics for telecom and data centers
These companies show the practical applications of photonic chips in real-world technology.
Advanced & Emerging Photonics
Photonics is rapidly evolving with technologies shaping the next generation of computing:
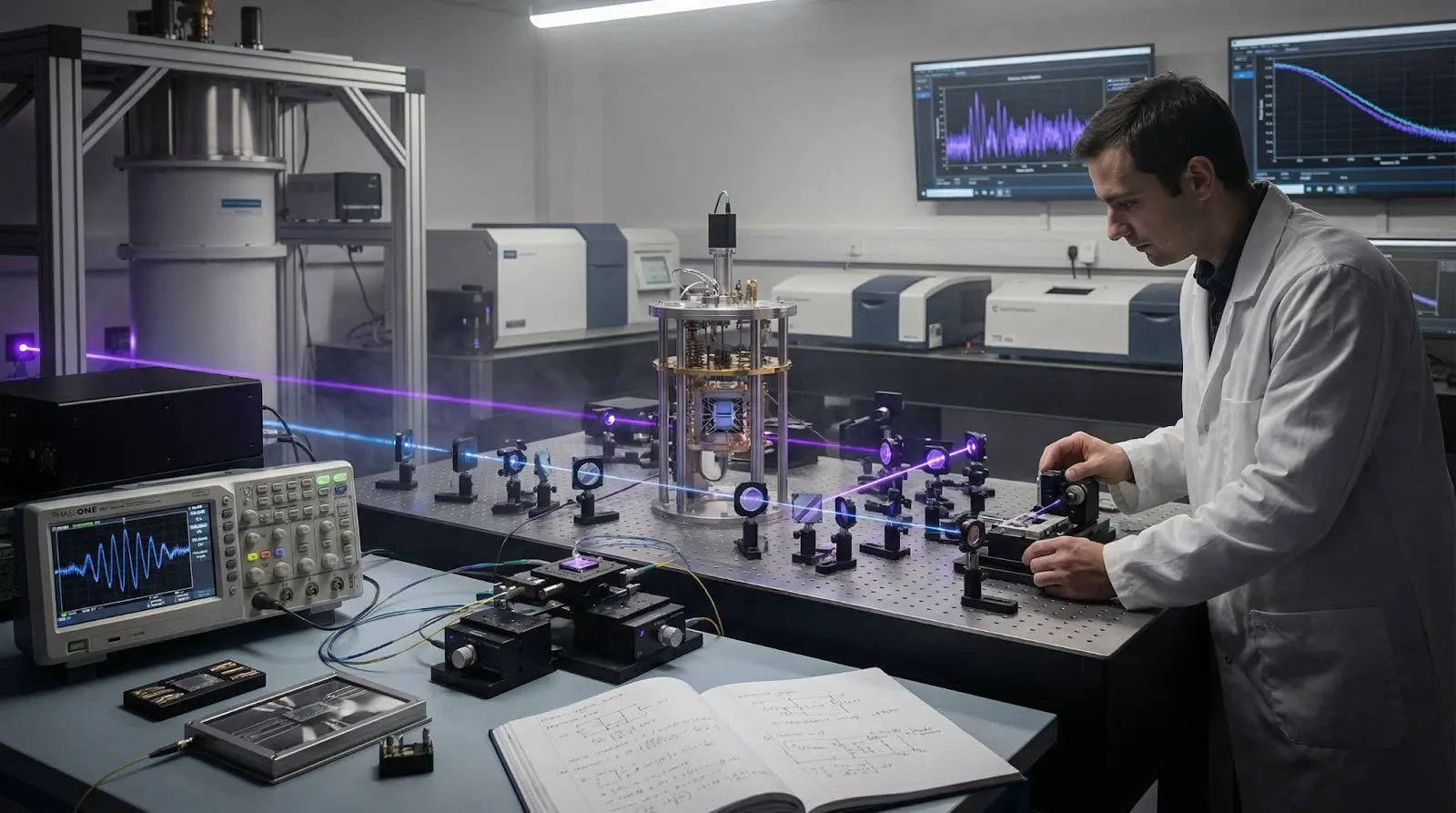

Integrated photonics – Entire optical systems on a single chip
Nano-photonic devices – Control light at the nanoscale
Quantum photonic chips – Fast, secure data processing for quantum computing
Advanced optical computing & next-generation photonic processors – Push speed and efficiency limits
Photonics + AI integration – Energy-efficient, high-performance AI systems
These advancements highlight the transformative potential of photonic chips for future technology.
Are Photonic Chip Marketers in India New and Trendy?
Yes. India’s Photonic chip development is emerging and gaining momentum, especially in research, system design, and optical networking. While India is not yet a global manufacturing leader in photonic chips, the ecosystem is new, promising, and actively growing.
Current Status of Indian Players
- Tata Elxsi – Actively involved in photonics R&D and system-level design, aligning with global photonics trends.
- Tejas Networks – Uses photonic technologies in optical networking and high-speed communication, a fast-growing and relevant application area.
- Sahasra Electronics – Works in semiconductor and electronic components, with early movement toward advanced technologies including photonics.
- CDAC – Plays a key role in research and development of photonics and optical computing concepts.
- IITs & IISc – Strong and well-recognized research in silicon photonics, making them major contributors to innovation rather than mass production.
Government programs like Make in India, Semicon India, and Digital India are pushing domestic semiconductor and photonics capabilities. These initiatives make photonic chips a future-focused and trending technology, especially for students, researchers, and startups.
Global Future Trends of Photonic Chips
The future of photonic chips looks very bright, thanks to the increasing need for high-speed data transfer across the globe. They are becoming essential for AI systems and data centers, providing fast, energy-efficient interconnects. With light-based processing, photonic chips reduce power consumption and heat compared to traditional electronic chips, making them ideal for sustainable, high-performance computing.
Silicon photonics enables cost-effective and scalable production, while photonic chips play a critical role in the telecom industry, including 5G and 6G, which require high-bandwidth communication. Strong investments from governments and industries ensures rapid innovation and widespread adoption. These clearly indicate that photonic chips are no longer a research area — they are the driving force behind the digital future.
Frequently Asked Quested (FAQ):
1. What is a photonic chip?
A photonic chip is a microchip that uses light (photons) instead of electricity to transmit, process, and store data, enabling faster and energy-efficient computing.
2. Where are photonic chips used?
Photonic chips are used in data centers, AI systems, telecom networks, optical computing, quantum computing, and high-speed communication technologies.
3. What companies manufacture photonic chips for data centers?
Global leaders include Intel, IBM, NVIDIA, Cisco, and Broadcom, which develop photonic chips for high-speed, energy-efficient data center application.
4. What are the top photonic chip products used in telecommunications networks?
Popular products include optical transceivers, co-packaged optics, silicon photonics modules, and high-speed optical interconnects from companies like Cisco, Broadcom, and Ciena.
5. Where can I buy photonic chips for AI applications?
Photonic chips for AI can be purchased through tech suppliers, distributors, or directly from manufacturers like Intel, NVIDIA, or specialized photonics startups. Some companies also offer evaluation kits for research and development.
Conclusion
Photonic chips are revolutionizing a major shift in computing technology. By using light instead of electricity, they offer higher speed, lower energy consumption, and better thermal performance.
From data centers and AI to telecommunications and quantum computing, photonic chips are shaping the future of digital systems. As research advances and costs reduce, photonic chips may soon become as common as electronic chips are today.
In simple terms: Photonic chips are not just an upgrade — they are the next revolution in computing.

Sorry, the comment form is closed at this time.